图的着色 -- 潘登同学的图论笔记
- 图的着色 > 对简单图G的每个顶点赋予一种颜色使得相邻的顶点颜色不同,称图G的一种点着色。对简单图G进行点着色所需的最少颜色数称为G的点色数,记为$χ(G)$
(注:对于n阶简单图,显然有$χ(G)≤n$)
边着色
对简单图G的每条边赋予一种颜色,使得相邻边颜色不同,称为图G的一种边着色
面着色
对无桥平面图图G的每个面赋予一种颜色,使得相邻的面颜色不同,称为图G的一种面着色
(利用对偶图,可以把平面图G的面着色问题转化为研究对偶图G'的点着色问题; 而通过下面的线图概念,也可以将图的边着色问题转化为点着色问题)
线图
假设G是简单图,构造图$L(G)$,G中的边和$L(G)$中的顶点一 一对应 ,如果G中的边$e_1和e_2$相邻,则L(G)中与$e_1和e_2对应的两个顶点间连一条边,称L(G)是G的线图
例子: (a)χ(G)=1 当且仅当G是离散图
(b)χ(Kn) = n
(c)(圈图)χ(Cn) = 2, n是偶数时, χ(Cn) = 3,n是奇数时 (n≥3)
(d)(轮图)χ(Wn) = 3 ,n是偶数时, χ(Wn) = 4,n是奇数时 (n≥3)
(e)χ(Gn)=2 当且仅当G是二部图
而点着色问题是NP完全问题Non-deterministic Polynomial,尚不存在有效的方法求解
(给出近似算法)
(算法)韦尔奇-鲍威尔算法 Welch_Powell(G)
输入: 简单图
输出:图G的一个着色方案
①将图中顶点按度数不增的方式排成排列
②使用一种新颜色对序列的一个顶点进行着色,并且按照序列次序,对与已着顶点不相邻的每一顶点着同样颜色,直至序列末尾。然后从序列中去掉已着色的顶点,得到一个新的序列
③对新序列重复步骤② , 直至得到空序列
上代码!!!
#%%韦尔奇-鲍威尔算法
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from Vertex import Vertex
from Graph import Graph
import matplotlib as mpl
class New_Vertex(Vertex): # 某一个具体问题的数据结构需要继承原有数据结构
def __init__(self, key):
super().__init__(key)
self.degree = 0 # 新增类属性(用于节点排序)
self.color = 'white' # 新增类属性(用于记录节点的颜色)
# 重写类方法
def addNeighbor(self, nbr, weight=0): # 增加相邻边,默认weight为0
'''
input:
nbr: Vertex object
weight: int
return:
None
'''
self.connectedTo[nbr] = weight
self.degree += 1
# 新增类方法 (查看degree)
def getDegree(self):
return self.degree
# 新增类方法, 设置节点颜色
def setColor(self, color):
self.color = color
# 新增类方法, 查看节点颜色
def getColor(self):
return self.color
class colorGraph(Graph):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
# 重载方法 因为原先Graph中新增节点用的是Vertex节点,但现在是用New_Vertex
def addVertex(self, key): # 增加节点
'''
input: Vertex key (str)
return: Vertex object
'''
self.numVertices = self.numVertices + 1
newVertex = New_Vertex(key) # 创建新节点
self.vertList[key] = newVertex
return newVertex
# 队列数据结构
class Queue():
def __init__(self):
self.queue = []
def enqueue(self, item):
self.queue.append(item)
def dequeue(self):
return self.queue.pop(0)
def isEmpty(self):
return self.queue == []
def size(self):
return len(self.queue)
def __iter__(self):
return iter(self.queue)
# 查看队首元素
def see(self):
return self.queue[0]
class Solution():
def createGraph(self, a_dict):
graph = colorGraph()
for i in a_dict:
for j in a_dict[i]:
graph.addEdge(i, j)
return graph
# 排序算法 -快速排序
def quickSort(self, a_list):
if len(a_list) <= 1: # 有可能出现left或者right是空的情况
return a_list
else:
mid = a_list[len(a_list)//2]
left = []
right = []
a_list.remove(mid)
for i in a_list:
if i[1] > mid[1]:
right.append(i)
else:
left.append(i)
return self.quickSort(left) + [mid] + self.quickSort(right)
def Welch_Powell(self, g):
queue = Queue()
Vertices_keys = g.getVertices()
Vertices_obj = [g.getVertex(k) for k in Vertices_keys]
# 用于储存顶点和他的degree
Vertices_deg = [[i, i.getDegree()] for i in Vertices_obj]
# 对Vertices_deg进行排序, 然后扔进队列里
for i in self.quickSort(Vertices_deg)[::-1]:
queue.enqueue(i[0])
# 当队列非空
color = 0 # 颜色标记
# 已着色顶点
color_done_vertex = []
while not queue.isEmpty():
# 对第一个点进行着色
frist_vertex = queue.dequeue()
frist_vertex.setColor(color)
color_done_vertex.append(frist_vertex)
for _ in range(queue.size()):
# 如果color_done_vertex与i这个节点有连接
Connections = []
for k in color_done_vertex:
Connections += list(k.getConnections())
if queue.see() in Connections:
# 将节点从队首加到队尾
queue.enqueue(queue.dequeue())
else:
temp = queue.dequeue()
temp.setColor(color)
color_done_vertex.append(temp)
color += 1
# 输出结果
result = []
while Vertices_obj:
temp_vertex = Vertices_obj.pop()
result.append((temp_vertex.getId(), temp_vertex.getColor()))
print(temp_vertex.getId(), ' 的颜色是:', temp_vertex.getColor())
return result
if __name__ == '__main__':
a_dict = {'a':['b', 'g', 'h'],
'b':['a', 'd', 'g', 'h'],
'c':['d', 'e'],
'd':['b', 'c', 'f'],
'e':['c', 'f'],
'f':['d', 'e'],
'g':['a', 'b', 'h'],
'h':['a', 'b', 'g']}
s = Solution()
graph = s.createGraph(a_dict)
result = s.Welch_Powell(graph)
G = nx.Graph()
for i in a_dict:
for j in a_dict[i]:
G.add_edge(i, j)
color = list(mpl.colors.TABLEAU_COLORS.values())
node_color = []
for i in result:
node_color.append(color[i[1]])
plt.clf()
pos = nx.spring_layout(G)
nx.draw(G, pos, node_color=node_color, font_size= 35,with_labels=True)
结果如下:
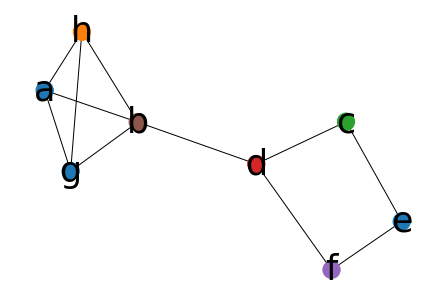
很明显这个不是最优解,把f可以换成棕色,c可以换成橙色,这样就用4种颜色来着色
之所以产生这样的问题,其一是:这个算法本身就是一种贪心策略的算法,难免会掉入局部最优
其次是这个算法的第一步是对顶点进行排序,排序的时候相同度数的顶点的顺序其实是不确定的,也会导致结果不优
图的着色就是这么多了,继续学习下一章吧!

